Africa Emerges as Hotspot for AI-Driven Fraud and Verification Innovation in Sumsub Identity Fraud Report 2025-2026
Attackers gain deepfakes, synthetic IDs, and autonomous fraud agents; defenders gain behaviour modelling, millisecond anomaly detection, and self-learning systems.”
JOHANNESBURG, GAUTENG, SOUTH AFRICA, November 27, 2025 /EINPresswire.com/ -- Deepfakes, synthetic identities, and cross-border fraud networks are on the rise, while businesses and regulators adopt AI-powered verification to safeguard Africa’s rapidly expanding digital economy.— Pavel Goldman-Kalaydin, Head of AI/ML at Sumsub
Sumsub, a global leader in digital identity verification, has released its highly anticipated Identity Fraud Report 2025-2026, providing an in-depth, data-driven view of identity fraud trends and prevention strategies across the globe, with a special focus on Africa. The report reveals how the continent’s rapid digital expansion is creating both unprecedented opportunities and complex challenges in the fight against fraud.
Key findings from the report:
Rising fraud markets:
o Mali: +131% YoY, 4.9% fraud rate
o Côte d’Ivoire: +51% YoY, 4.5%
o Malawi: +49% YoY, 4.0%
o Cameroon: +18% YoY, 4.9%
o Uganda: +3% YoY, 4.7%
o Senegal: +28% YoY, 4.2%
Declining fraud markets:
o Nigeria: –54% YoY, 2.7% (largest drop)
o Algeria: –60% YoY, 2.3%
o Kenya: –42% YoY, 2.3%
o South Africa: –31% YoY, 1.4%
South Africa’s decline was driven by advanced regulatory frameworks and improved verification systems. However, deepfake incidents rose 269% YoY, signalling a shift toward AI-enabled impersonation as the emerging threat.
In 2025, Africa’s digital economy is booming. Mobile money, fintech platforms, and e-government services are driving financial inclusion at scale, but this growth has also made the continent a prime battleground for identity fraud. While low-effort scams are declining due to stronger verification systems, fraudsters have shifted toward more sophisticated attacks: deepfake-enabled liveness bypasses, synthetic identity rings, and coordinated post-KYC abuse are increasingly common.
“AI reshapes both offence and defence. Attackers gain deepfakes, synthetic IDs, and autonomous fraud agents; defenders gain behaviour modelling, millisecond anomaly detection, and self-learning systems. The next frontier is verification of AI agents themselves — confirming not just who you are, but who acts on your behalf,” said Pavel Goldman-Kalaydin, Head of AI/ML at Sumsub.
Deepfake-based attacks have emerged as the most dynamic and worrying trend. In the Democratic Republic of Congo, deepfake attempts increased 367% year-on-year, Malawi 325%, and Tanzania 317%. The most striking deepfake growth was in Zambia (967%). In Kenya, deepfakes now account for nearly 10% of all fraud attempts. Across Africa, nearly one in five people have been directly targeted by deepfake attacks, while 24% of respondents admitted they cannot reliably distinguish them.
“The Sophistication Shift is evident across the continent. Fraudsters are moving from high-volume, low-effort scams to highly targeted, AI-driven operations. At the same time, African businesses and regulators are innovating fast, with enhanced SIM–ID linkages, behavioural analytics, and cross-border cooperation,” said Hannes Bezuidenhout, Sumsub VP for Sales Africa. “Africa’s story is not only about exposure — it is about resilience, innovation, and a shared commitment to building digital trust from the ground up.”
Nigeria’s trajectory is particularly notable: overall fraud fell sharply by 54% YoY to 2.7%, driven by strict enforcement of NIN–SIM linkage and aggressive cybercrime crackdowns. Despite this improvement, certain risks persist. Anti-money laundering (AML) incidents remain elevated at 4%, reflecting the continued sophistication of attackers who now target stronger defences with AI-enhanced techniques. Deepfakes, while not yet as widespread as in some other markets, represent an emerging vector for highly targeted attacks, demonstrating that even countries showing overall decline face complex, high-skill fraud challenges.
Consumer and business insights
Sumsub’s survey shows that 92% of African consumers would only use service providers with strong anti-fraud measures. Finance, travel, and e-commerce sectors remain the most trusted industries, while iGaming, crypto, social media, and dating platforms face scepticism due to frequent breaches and unclear accountability. Phishing (57%) and social engineering (38%) were the most reported attack vectors, resulting in social media account takeovers (45%) and financial theft (42%).
Businesses report high levels of both first-party fraud (when the individual behind the verification is the fraud actor) and third-party fraud (when external attackers exploit or impersonate genuine users). Account takeover, identity theft, and phishing are prevalent, while customers increasingly exploit synthetic identities and deepfakes for application and chargeback fraud. Nearly nine in ten businesses acknowledge that fraud is becoming more sophisticated due to AI and deepfake technologies, with 76% reporting more frequent organised fraud attempts.
Regional case studies
Mozambique: Former Finance Minister sentenced to 8.5 years for a $2 billion cross-border fraud scheme.
INTERPOL’s Operation Serengeti 2.0 dismantled cyber fraud networks across 18 African countries, recovering $97.4 million.
West Africa: Human trafficking-linked scam centres are expanding, leveraging AI-generated visuals and automated chatbots to enhance social engineering.
Sophistication Shift in Africa’s Fraud Landscape
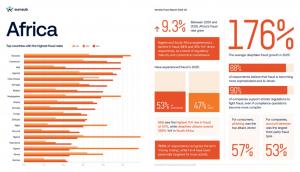
Africa’s fraud ecosystem is undergoing a structural shift marked by a 180% increase in sophisticated attacks compared with 2024, featuring advanced deception, AI-generated identities, targeted social engineering, and multi-stage attack chains. Low-effort, mass-volume scams have largely been neutralised by improved verification systems.
Three dynamics stand out:
1. Less amateur fraud, more high-skill attacks: Stronger KYC/AML platforms have raised entry barriers, rendering simple impersonation or document fraud ineffective. Fraudsters now invest more time and resources, causing fewer but more damaging incidents.
2. Technology outpaces awareness: Citizens and businesses struggle to keep up with rapidly evolving threats, especially generative AI-based scams.
3. Strategic, resource-intensive operations: Automated defences intercept low-effort scams early, pushing determined actors toward complex, tailored attacks exploiting human behaviour, biometrics, or system gaps.
Sumsub Fraud Exposure Survey 2025 highlights:
o 53% of African businesses and 47% of users experienced fraud in 2025.
o Among consumers, phishing was the top attack vector (57%).
o For companies, account takeover was the leading third-party fraud type (53%).
o 87.5% of respondents believe fraud is becoming more sophisticated and AI-driven.
o 76.5% of respondents recognise “money muling,” and 1 in 4 individuals have been personally targeted.
o 90% of companies support stricter anti-fraud regulations, even if compliance becomes more complex.
Deepfakes: A growing threat
High-adoption markets like Kenya and Nigeria show declining overall fraud, but deepfakes account for a significant portion of remaining attacks, illustrating fraudsters targeting the strongest defences.
Global challenge, local realities
Fraud patterns vary across regions. Sumsub’s data offers insights into how local conditions influence exposure and prevention, highlighting the shared challenges posed by AI-driven fraud globally.
The Sumsub Identity Fraud Report 2025-2026 demonstrates that Africa is no longer a passive observer in the global fight against fraud. Instead, it is shaping new standards of verification and resilience in a digital-first world.
A New Era of AI-Driven Fraud in 2026
Sumsub forecasts a decisive shift in the global fraud landscape in 2026, with attacks becoming more sophisticated, automated, and damaging despite a possible decline in overall volumes. Fraudsters are expected to rely heavily on advanced AI tools, including autonomous agents capable of probing systems, generating synthetic identities, and imitating genuine user behaviour at scale.
“Identity verification is entering a new phase — one where automation, AI and data fusion converge,” says Sumsub CTO Vyacheslav Zholudev. He notes that next year’s major breakthroughs “won’t come from better document scanning, but from AI agents verifying other AI agents.” As digital assistants increasingly conduct transactions on behalf of users, businesses will require systems that can confirm both the individual and the entity acting on their behalf — securely and traceably.
Money mule networks are also expected to multiply, with fraud rings using AI to coordinate thousands of accounts that blend into high-volume industries such as fintech, e-commerce and iGaming. Social engineering risks will escalate through AI-powered phishing, voice spoofing, and impersonation, particularly in markets with lower digital literacy.
The report emphasises that fragmented compliance tools are no longer viable. Verification will move beyond single-step checks into continuous assessment, drawing on device telemetry, behavioural analytics, and contextual intelligence. Zholudev argues that trust “must evolve with every interaction,” and that unified compliance and fraud prevention ecosystems will become essential as organisations merge risk, fraud and compliance into a single intelligence function.
To explore Sumsub Identity Fraud Report 2025-2026 in full detail, please get your free copy at https://sumsub.com/fraud-report-2025/
About Sumsub
Sumsub is a leading full-cycle verification platform that enables fraud-free, scalable compliance. Its adaptive, no-code solution covers everything from identity and business verification to ongoing monitoring – quickly adjusting to evolving risks, regulations, and market demands.
Recognized as a Leader by Gartner, Liminal, and KuppingerCole, Sumsub combines seamless integration with advanced fraud prevention to deliver industry-leading performance.
Sumsub has over 4,000 clients across the fintech, crypto, transportation, trading, e-commerce, education, and gaming industries, including Bitpanda, Wirex, Avis, Bybit, Vodafone, Duolingo, Kaizen Gaming, and TransferGo.
ends
Elize Engle
Tishala Communications
+27 63 574 5249
email us here
Legal Disclaimer:
EIN Presswire provides this news content "as is" without warranty of any kind. We do not accept any responsibility or liability for the accuracy, content, images, videos, licenses, completeness, legality, or reliability of the information contained in this article. If you have any complaints or copyright issues related to this article, kindly contact the author above.